A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Printing – Supplies, Materials, and Considerations
3D printing has emerged as a versatile and efficient method of production, offering a plethora of possibilities across various industries. However, diving into the world of 3D printing entails more than just acquiring a printer and filament. This comprehensive guide delves into the essential supplies, types of printing materials, costs, and considerations associated with 3D printing.
Understanding Basic 3D Printer Supplies
To embark on a 3D printing journey, one must first acquire a suitable printer. Several types of printers cater to different needs, ranging from Stereolithography (SLA) and Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) to Digital Light Printing (DLP) and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). Each type offers unique capabilities and is suitable for various applications, from hobbyist projects to industrial-grade manufacturing.

In addition to the printer itself, several accessories are essential for seamless operation. These include storage containers for printing materials to maintain their integrity, adhesives for securing prints during the printing process, build plates to enhance adhesion and surface finish, and ventilation equipment to mitigate potential health hazards from fumes.
Furthermore, a set of precision tools such as calipers and a toolset for maintenance and repairs are indispensable for ensuring the quality and longevity of 3D printers.
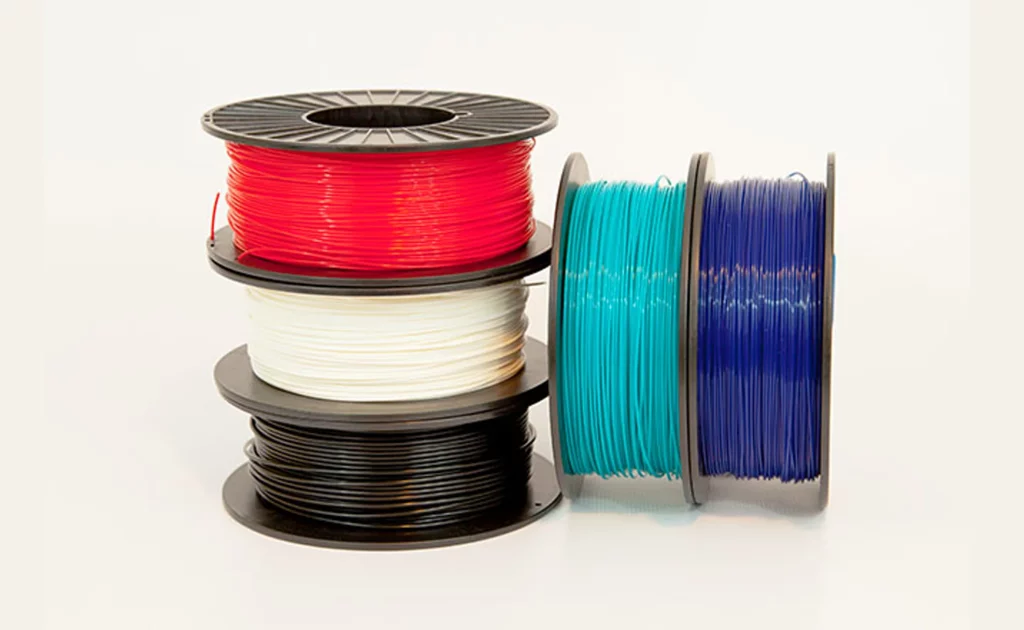

Types of Printing Materials
The choice of printing material significantly influences the outcome of 3D printing projects. Common materials include plastics, powders, resins, metals, and other composite materials like carbon fibre and graphene.
Plastics
Plastics, particularly Polylactic acid (PLA) and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), are widely used for their affordability and versatility. PLA, derived from natural sources, is eco-friendly and suitable for a range of products, while ABS offers durability and safety, making it ideal for consumer goods.
Powders
Powder-based materials like polyamide and alumide offer strength and flexibility, enabling intricate designs and industrial applications.
Resins
Resins, though less commonly used, provide high detail and smooth finishes, making them suitable for small-scale models and aesthetic prints.
Metals
Metal printing, facilitated by techniques like Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), offers unparalleled strength and durability, making it ideal for aerospace and industrial components.
Considerations and Costs
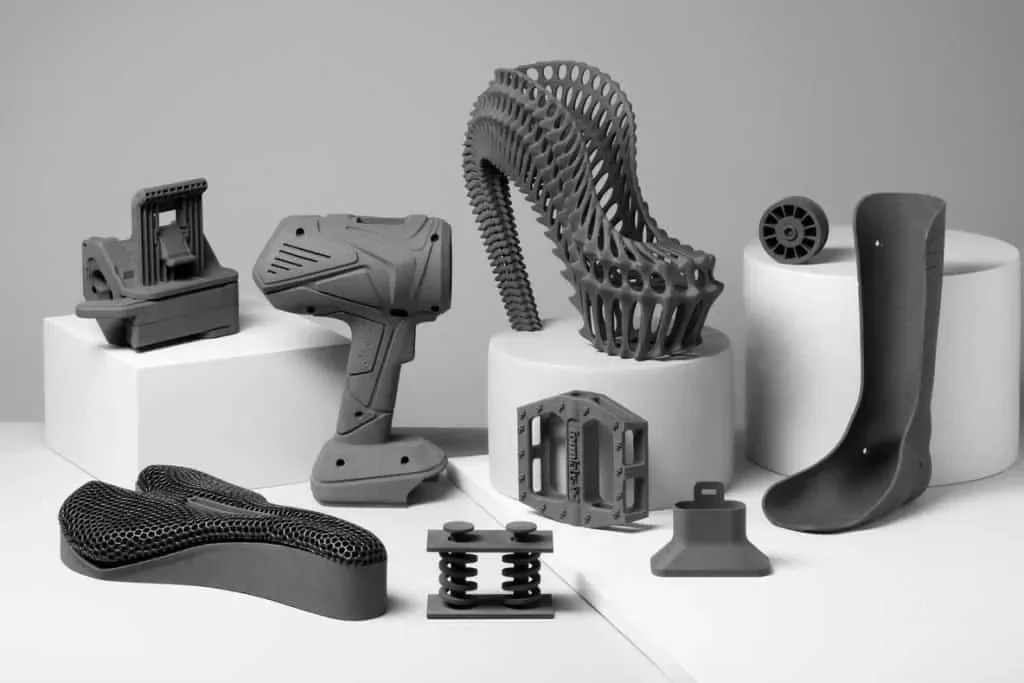

While 3D printing presents cost-saving opportunities, it also entails significant expenses beyond the initial investment in the printer. Factors such as printer type, printing materials, and accessories contribute to the overall cost of 3D printing.
The cost of 3D printers varies widely, ranging from consumer-grade models priced at several hundred dollars to industrial-grade machines costing tens of thousands of dollars. Similarly, printing materials range from affordable options like PLA filament to specialty materials like metal and carbon fibre, which command higher prices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 3D printing offers a world of possibilities across various industries, from rapid prototyping to custom manufacturing. However, to harness the full potential of 3D printing, one must invest in the necessary supplies, understand the different types of printing materials, and consider the associated costs and considerations.
With the right equipment, materials, and knowledge, individuals and businesses can unlock endless opportunities for creativity and innovation through 3D printing.
